Endoscopic Approach for Cervical Disease: Successful Points
Article information
Abstract
The advent of endoscopic technology has facilitated the evolution of endoscopic techniques and broadened the indications of fully endoscopic spine surgery. Endoscopic cervical spinal surgery is currently effective for treating herniated intervertebral discs, foraminal stenosis, and central canal stenosis. Although growing evidence has revealed the safety and advantages of endoscopic approaches, fully endoscopic spine surgical procedures remain challenging and have a steep learning curve, especially in the cervical spine. The anatomical features and pathologic patterns of the cervical spine also affect the application of endoscopic approaches. In this review, the authors introduce the successful points of fully endoscopic cervical spine surgery.
INTRODUCTION
Cervical intervertebral disc herniation, stenosis with radiculopathy or myelopathy are common degenerative spine diseases causing disability in working and daily activities [1]. Surgical intervention is indicated when patients are disable due to pain refractory to conservative treatments, profound motor weakness, or gait disturbance. The conventional surgeries include anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), posterior decompressive laminectomy with or without fusion, or laminoplasty according to the main pathologies. These approaches have been studied and validated exhaustively [2-6]. ACDF have been the gold standard of cervical disc operation, but fusion of vertebrae may cause development of adjacent disc disease and may need further surgical intervention [7]. Besides, the endoscopic approach can decompress the neural structure and preserve the mobility simultaneously [8]. With development of endoscopic equipment and surgical technique, it has been applied to cervical spinal surgeries. Currently, there are different endoscopic systems for the spinal surgeries. According to the consensus of nomenclature, endoscopic spine surgery is classified into mainly 2 categories, including full-endoscopic and endoscopy-assisted surgeries. Full-endoscopic spine surgery refers to the surgery performed with a working channel endoscope through a single incision. Biportal endoscopic spine surgery is an emerging alternative by different ports for endoscope and working channel. In the current review, the authors will focus on the full-endoscopic approach in the cervical spinal disease treatment.
CERVICAL DISEASES INDICATED FOR FULL-ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES
The common cervical diseases indicated for full-endoscopic approaches are degenerative diseases, including herniated intervertebral disc, foraminal stenosis, or central canal stenosis. The degeneration of cervical intervertebral disc, osteophytes from uncovertebral joints, and hypertrophic facet joints causes the cervical myelopathy or radiculopathy. Cervical spinal stenosis can also result from the buckling ligamentum flavum and narrowed intervertebral foramen. Older patients tend to suffer from etiology of degenerative osteophytes while the etiology of younger patients are from herniation of intervertebral disc [9].
Patients with cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy concordant to the radiological images are indicated for surgical intervention when conservative treatments fail [10]. Currently, full-endoscopic cervical spine surgeries are indicated for decompression surgeries, including discectomy, foraminotomy, and laminotomy. The routes of the endoscopic approaches are anterior or posterior approach. The cervical endoscopic approaches include anterior endoscopic cervical discectomy (AECD), anterior endoscopic transcorporeal discectomy (AETD), posterior endoscopic cervical discectomy (PECD), cervical endoscopic unilateral laminectomy and bilateral decompression (CE-ULBD), and posterior endoscopic cervical foraminotomy (PECF). Surgeons can determine the approach according to the characteristics and zone of the pathology.
The indication of AECD is cervical radicular pain due to soft disc herniation without narrowed intervertebral space, calcified disc, spondylolisthesis, or osteophytes. Because of the limited surgical fields by intervertebral space, AECD is effective in removing the herniated disc without migration. For the migrated disc herniation, AETD is an alternative to remove the sequestrated disc only by creating a bony channel through the vertebral body rather than through the disc space. This approach can help preserve the cervical motion segment and preserve the disc. For patients with foraminal stenosis or foraminal disc herniation, PECF or PECD could be an alternative to decompress the nerve root. CE-ULBD is effective in solving central canal stenosis causing myelopathy.
ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS FOR SUCCESSFUL CERVICAL ENDOSCOPIC SURGERIES
From the current evidence, the efficacy of endoscopic surgery is comparable to standard surgeries. The benefits of the endoscopic approaches are safety and enhancing recovery by minimizing the tissue trauma and complications. However, the endoscopic approaches in cervical spine are under development and technically demanding. An inexperience surgeon may encounter failure or complication risks in cervical endoscopic surgeries.
1. Patient Selection
Patient selection is an essential and first step for endoscopic surgery. Patients with degenerative cervical spinal diseases may have variable clinical presentations, such as neck pain, radiating pain to arms or hands, numbness, motor weakness, or spastic gait. Sometimes, it is difficult to identify the pain generator according to clinical presentation and radiological images. Besides, some patients having multilevel diseases may confuse the diagnosis and surgical plans. Selective nerve block by epidural injection could help differential diagnosis. When the target lesions are multilevel in the cervical spine, surgeons have to weigh benefits of endoscopic approaches in the complex situation. In general, patients with single level disease are ideal for endoscopic approach.
Herniated or sequestrated disc, especially soft disc, is the standard indication for cervical endoscopic approach. The operators should evaluate the radiological studies and exclude patients with calcified discs, prominent osteophytes, or ossification of posterior longitudinal ligaments. The dynamic radiography is also mandatory to confirm stability. Currently, there is no guideline for decision of surgical approach and the surgical approach depends on surgeon’s experience. However, patients with previous neck surgeries or radiotherapy may limit the application of the anterior approach. The esophagus and carotid artery are vulnerable to injury while inserting the puncture needle or obturator through the scarring or stiff soft tissue. Sagittal alignment and disc height should be evaluated before AECD. The narrowed disc space (less than 5 mm) or significant cervical kyphosis may restrict the corridor of AECD, and PECD or fusion could be an alternative [11-14]. Although full-endoscopic ACDF is feasible, instrumentation for internal fixation is not available in the cervical endoscopic fusion system. Therefore, standard ACDF with instrumentation is more reasonable for patients with instability noted on radiography.
2. Determine the Approach
Currently, there are no definite rules for the decision of surgical approach regarding cervical endoscopic discectomy. The indication of the anterior endoscopic approach is restricted, and most surgeons are unfamiliar with the anterior endoscopic approach. The first key step in the anterior approach is the percutaneous docking of the endoscope under fluoroscopic guidance. The surgeon can push the esophagus and carotid artery by the index and middle finger, respectively, and a cannulated needle can be inserted into the space between the 2 fingers. The trajectory of the cannulated needle is toward the target lesion directly and lands on the posterior annulus of the index intervertebral disc. The manipulation should be gentle and avoid plunging the endoscope into the canal during the endoscopic procedures. The endoscopic holder can help to stabilize the instrument and prevent a bump to the cervical spinal cord (Figure 1)
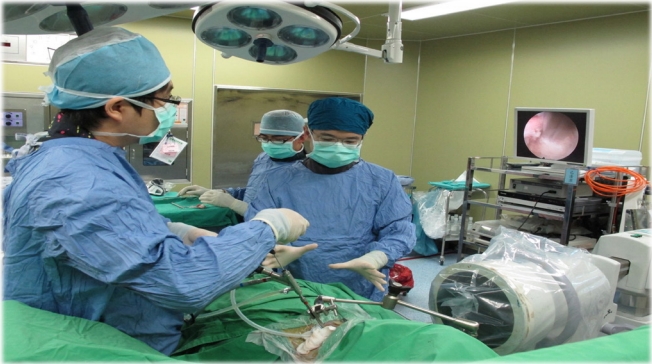
The endoscopic holder can help the surgeon stabilize instruments during procedures and prevent incidental strikes to the cervical spinal cord. This figure was provided by the corresponding author and consented for publications.
Although the diameter of the working cannula is smaller in the OECD, the risk of injury to the intervertebral disc due to passing the working cannula may cause the progression of degeneration, and subsequent revision may be necessary for long-term follow-up. Besides, though injuries to the carotid artery or esophagus are rare, the potential risk of major complications remains. On the contrary, the carotid artery and esophagus are free from injury during the posterior approach. Besides, preserving the intervertebral disc is better during the posterior approach. The indications of posterior endoscopic cervical spinal surgery have been expanded to decompress all kinds of pathologies with the techniques of foraminotomy and laminotomy. Therefore, more surgeons have used the posterior approach in endoscopic cervical spinal surgery in recent years.
3. Control of Flow and Pressure of Saline Infusion
The endoscopic spinal surgery requires continuous saline irrigation during the surgery. A proper flow of saline irrigation can ensure clear endoscopic visualization. The excessive saline infusion can increase epidural pressure as well as intracranial pressure (ICP) [15], and it may cause symptoms of increased ICP or induce seizure [16]. The increased pressure by saline irrigation usually results from the uncontrolled infusion pressure or obstruction of outflow tract. The operator should make sure that the outflow of saline irrigation is smooth. The normal saline bag can be elevated higher above the surgical wound or be compressed for a higher-pressure during bleeding to achieve a clearer vision temporarily. If dura tear occurs, it would form a connecting pipeline. ICP can further increase due to inflow of saline through the dural defect. Patients might have severe headache, significantly increased blood pressure, seizure, or even change of consciousness [16]. The infusion flow of saline irrigation should be decreased immediately for a lower pressure to avoid the critical situation [17].
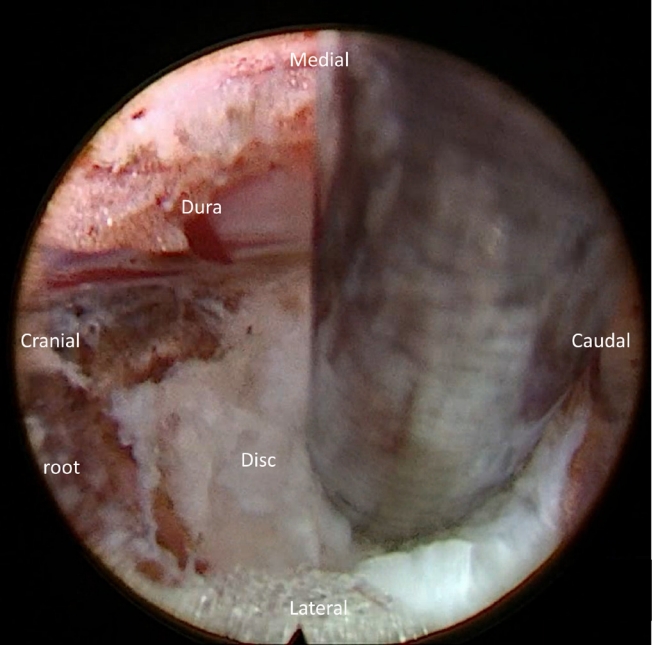
4. Minimize Dura Sac Manipulation
The cervical cord is vulnerable to manipulation during the endoscopic spine surgery. Therefore, retraction or manipulation of neural structure or dural sac should be minimized or avoided [18]. For foraminal disc herniation, manipulation of dural sac or root is usually unnecessary after adequate posterior foraminotomy (Figure 2). Different approaches are necessary to be able to reach target lesion and spare manipulating the spinal cord during the cervical endoscopic surgery. Usually, the contained disc herniation at central region can be resected by anterior approach. Patients with paramedian or foraminal herniated discs are ideal candidates for posterior approach. High grade migration of cervical disc herniation is challenging both for anterior and posterior approach. Therefore, modified techniques with different trajectories have been reported in the previous literature. Though there is limited evidence, anterior transcorporeal approach can be an alternative to approach highly migrated disc at the cervical spine [19].
5. Create Working Space: Medial Facetectomy, Retrocorporeal Approach
To avoid manipulation to cord or roots and to achieve adequate decompression, another surgical strategy is creating the space by removal of the osseous structure. Surgeons have to balance the extent of bone removal to increase working space and the possibility of iatrogenic instability [20,21]. The advent of endoscopic burr expanded the indications of the full-endoscopic spine surgery. Kim et al. [22] reported favorable clinical and radiological results on cervical radiculopathy of 30 patients by applying partial pediculotomy and partial vertebrotomy for posterior endoscopic cervical foraminotomy. The partial resection of superior pedicle and posterior vertebrae could avoid violating the motion segment of the cervical spine. Ou et al. [23] also proposed similar concept by hemilaminectomy and partial retrocorporeal resection with endoscopic burr. In this way, it is feasible to approach central disc herniation or migrated disc without manipulating the dural sac through posterior approach (Figure 3). These modified techniques can widen the working space to ensure the safety during the removal of herniated disc.
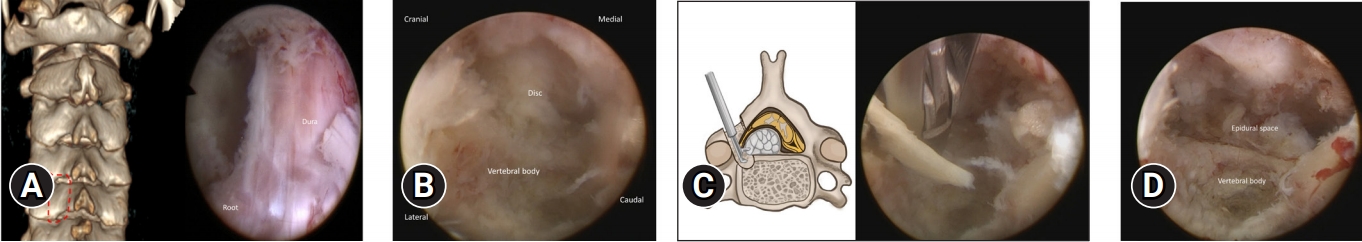
Modified posterior endoscopic cervical discectomy for a highly migrated disc herniation. (A) Hemilaminectomy to create the working zone. (B) After drilling the posterior vertebral body, the epidural space was expanded. (C) The retrocorporeal approach can help remove the migrated disc without manipulating the dural sac. (D) After removal of migrated fragment, the epidural space was vacant, with a pulsatile dural sac.
Though major vessel injury is rare in endoscopic spinal surgery, there is a potential risk of injury to the vertebral artery (VA). The VA usually runs in the transverse foramina of the C1–6 vertebrae and supplies blood to the hindbrain. It is important to avoid major vessel injury by understanding the anatomy of the VA. The course of VA is more medial and closer to lateral recess at the caudal level and closer to the left than the right side [24]. The VA is anterior to the exiting root and lateral to the pedicle. The safe zone between the lateral pedicle border and VA is around 1–2 mm from C2 to C6 but is only 0.65mm at the C6–7 level [25]. Therefore, keeping the surgical field within the lateral pedicle line is safe while bypassing the exiting nerve root to remove the disc or ventral osteophytes.
CONCLUSION
The goal of the endoscopic spine surgery is the effective decompression with a minimal invasiveness. Targeted-oriented approach is essential while deciding the surgical trajectory. Though the indications of cervical endoscopic spine surgeries have been expanded, adequate patient selection according to operators’ techniques and experience is critical and the first step to the success. The working space is smaller in the cervical spine than in the lumbar spine, and complications could be devastating with cervical cord injury. Different approaches are necessary to be able to reach every area of the spinal canal without manipulating the spinal cord. Modified techniques to widen the canal by partial resection of the surrounding bony structures can provide a safe corridor to reach the lesion. A meticulous protocol and further studies to prove its efficacy and safety are necessary.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.